Coursera - Computer Science: Programming With A Purpose
Week 9: Creating Data Types - Color Data Type
Write a data type ColorHSB.java that represents a color in hue–saturation–brightness (HSB) format, along with a sample client. The HSB color format is widely used in color pickers.
HSB = (240°, 100%, 100%)
A color in HSB format is composed of three components:
- The hue is an integer between 0 and 359. It represents a pure color on the color wheel, with 0° for red, 120° for green, and 240° for blue.
- The saturation is an integer between 0 and 100. It represents the purity of the hue.
- The brightness is an integer between 0 and 100. It represents the percentage of white that is mixed with the hue.
Implement the following public API:
public class ColorHSB {
// Creates a color with hue h, saturation s, and brightness b.
public ColorHSB(int h, int s, int b)
// Returns a string representation of this color, using the format (h, s, b).
public String toString()
// Is this color a shade of gray?
public boolean isGrayscale()
// Returns the squared distance between the two colors.
public int distanceSquaredTo(ColorHSB that)
// Sample client (see below).
public static void main(String[] args)
}
Here is some more information about the required behavior:
- Corner cases. Throw an IllegalArgumentException in the constructor if any component is outside its prescribed range (0 to 359 for the hue, 0 to 100 for the saturation and brightness); throw an IllegalArgumentException in distanceSquaredTo() if its argument is null.
- String representation. Return a string composed of the integers for hue, saturation, and brightness (in that order), separated by commas, and enclosed in parentheses. An example is (26, 85, 96).
- Grayscale. A color in HSB format is a shade of gray if either its saturation or brightness component is 0% (or both).
-
Distance. The squared distance between two colors (h1,s1,b1) and (h2,s2,b2) is defined to be
min { (h1 − h2) 2 , (360 − |h1 − h2|) 2 } + (s1 − s2) 2 + (b1 − b2) 2
For example, the squared distance between (350, 100, 45) and (0, 100, 50) is 10 2 + 0 2 + 52 = 125.
-
Sample client. The main() method should take three integer command-line arguments h, s, and b; read a list of pre-defined colors from standard input; and print to standard output the pre-defined color that is closest to (h,s,b).
-
Input specification. The input from standard input consists of a sequence of one or more lines. Each line contains a string (the name of a pre-defined color) and three integers (its hue, saturation, and brightness components), separated by whitespace. The data files web.txt and web.txt are in the specified format.
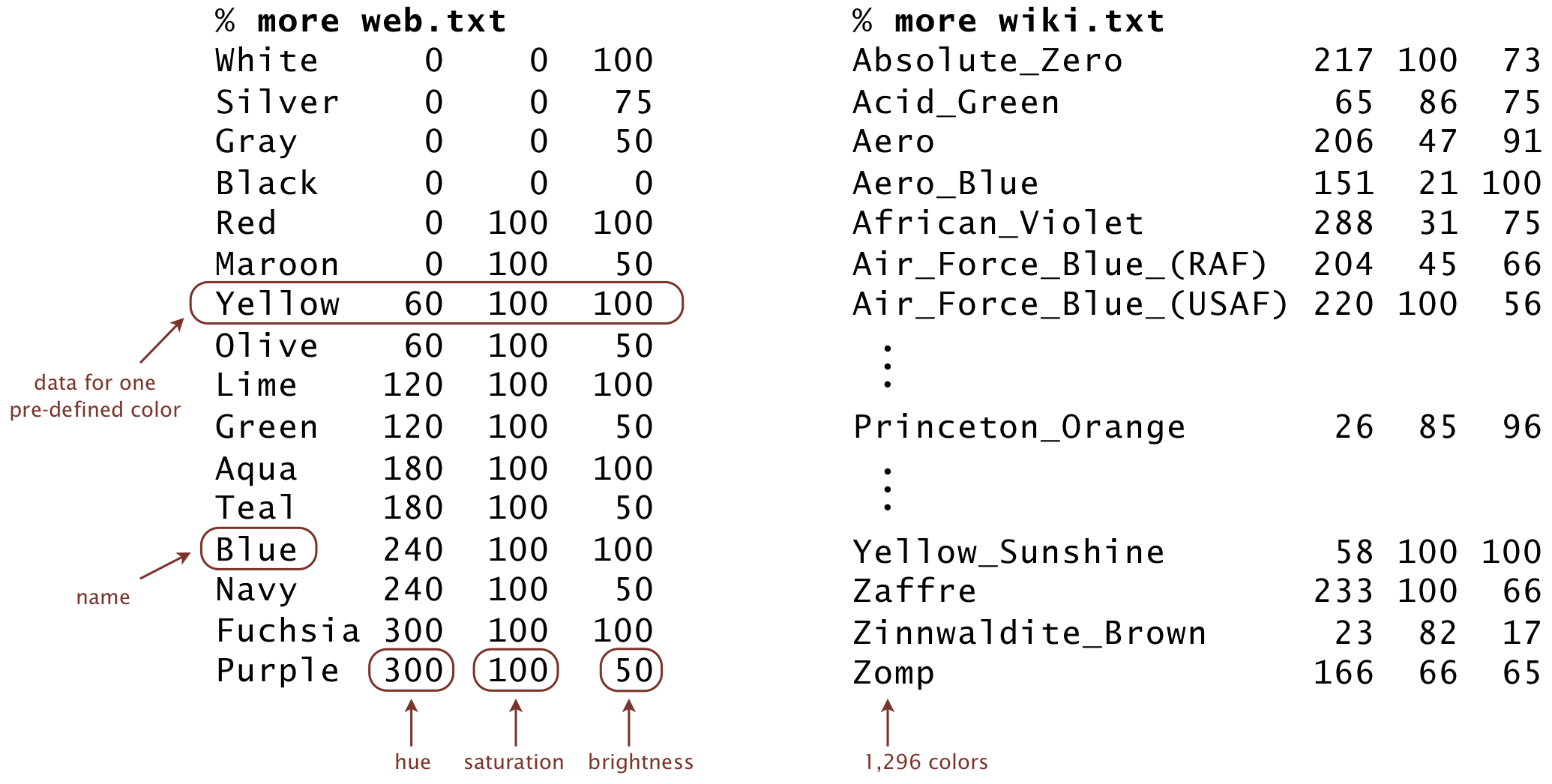
-
Output specification. The output to standard output consists of one line: the name of the nearest pre-defined color and the string representation of that color, separated by whitespace.
-
~/Desktop/oop2> java ColorHSB 25 84 97 < web.txt
Red (0, 100, 100)
~/Desktop/oop2> java ColorHSB 350 100 45 < web.txt
Maroon (0, 100, 50)
~/Desktop/oop2> java ColorHSB 25 84 97 < wiki.txt
Princeton_Orange (26, 85, 96)
Note: the above description is copied from Coursera and converted to markdown for convenience
Solution:
public class ColorHSB {
private static final int MAX_HUE = 359;
private static final int MAX_SATURATION = 100;
private static final int MAX_BRIGHTNESS = 100;
private final int hue; // 0...359, 0 = red, 120 = green, 24 = blue
private final int saturation; // 0...100
private final int brightness; // 0...100
// Creates a color with hue h, saturation s, and brightness b.
public ColorHSB(int h, int s, int b) {
if ((h < 0) || (h > MAX_HUE)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if ((s < 0) || (s > MAX_SATURATION)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if ((b < 0) || (b > MAX_BRIGHTNESS)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
hue = h;
saturation = s;
brightness = b;
}
// Returns a string representation of this color, using the format (h, s, b).
public String toString() {
return "(" + hue + ", " + saturation + ", " + brightness + ")";
}
// Is this color a shade of gray?
public boolean isGrayscale() {
return (saturation == 0) || (brightness == 0);
}
// Returns the squared distance between the two colors.
public int distanceSquaredTo(ColorHSB that) {
if (that == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
return (int) (Math.min(Math.pow(hue - that.hue, 2), Math.pow(360 - Math.abs(hue - that.hue), 2))
+ Math.pow(saturation - that.saturation, 2)
+ Math.pow(brightness - that.brightness, 2));
}
// Sample client (see below).
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int h = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
final int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
final int b = Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
final ColorHSB colorHSB1 = new ColorHSB(h, s, b);
int closestDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
String closestColorName = null;
ColorHSB closestColorHSB = null;
while (StdIn.hasNextLine() && !StdIn.isEmpty()) {
final String colorName = StdIn.readString();
final int h2 = StdIn.readInt();
final int s2 = StdIn.readInt();
final int b2 = StdIn.readInt();
final ColorHSB colorHSB2 = new ColorHSB(h2, s2, b2);
final int distance = colorHSB1.distanceSquaredTo(colorHSB2);
if (distance < closestDistance) {
closestDistance = distance;
closestColorName = colorName;
closestColorHSB = colorHSB2;
}
}
StdOut.println(closestColorName + " " + closestColorHSB);
}
}
Link To: Java Source Code