Coursera - Computer Science: Programming With A Purpose
Week 7: Performance - Inversions
Suppose that a music site wants to compare your song preferences to those of a friend. One approach is to have you and your friend each rank a set of n songs and count the number of pairs of songs (i, j) for which you prefer i to j but your friend prefers j to i. When the count is low, the preferences are similar.
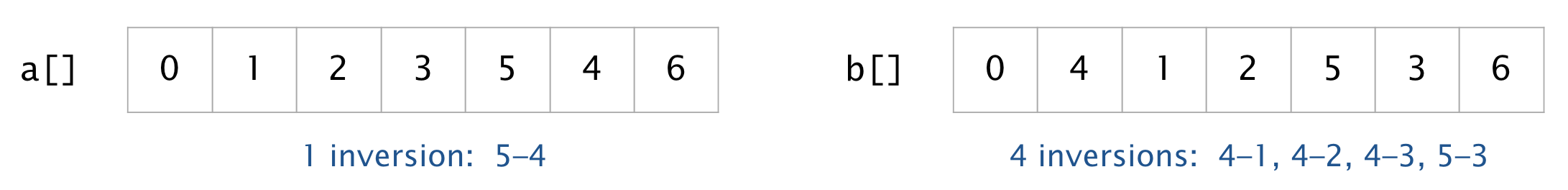
More generally, given an array of integers, a pair of elements a[i] and a[j] are inverted if i < j and a[i] > a[j]. For example, the array a[ ] has 1 inversion and the array b[ ] has 4 inversions.
Write a program Inversions.java that implements the following API:
public class Inversions {
// Return the number of inversions in the permutation a[].
public static long count(int[] a)
// Return a permutation of length n with exactly k inversions.
public static int[] generate(int n, long k)
// Takes an integer n and a long k as command-line arguments,
// and prints a permutation of length n with exactly k inversions.
public static void main(String[] args)
}
Here is some more information about the required behavior:
- Permutations. A permutation of length n is an integer array of length n that contains each of the n integers 0, 1, …, n – 1 exactly once.
- Output format. The main() method should print the permutation of length n to standard output as a sequence of n integers, separated by whitespace, all on one line.
- Performance. The count() method should take time proportional to n2 in the worst case. The generate() method should take time proportional to n in the worst case.
- Corner cases. You may assume that the arguments to generate() satsify n ≥ 0 and 0 ≤ k ≤ 12n(n − 1); this guarantees the existence of a permutation of length n with exactly k inversions.
Here are a few sample executions:
~/Desktop/performance> java Inversions 10 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
~/Desktop/performance> java Inversions 10 1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 8
~/Desktop/performance> java Inversions 10 45
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
~/Desktop/performance> java Inversions 10 20
9 8 0 1 2 3 7 4 5 6
Counting inversions arise in a number of applications, including sorting, voting theory, collaborative filtering, rank aggregation, and non-parametric statistics.
Note: the above description is copied from Coursera and converted to markdown for convenience
Solution:
public class Inversions {
// Return the number of inversions in the permutation a[].
// Max time complexity = O(n2)
public static long count(int[] a) {
long count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (a[i] > a[j]) {
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
// Return a permutation of length n with exactly k inversions.
// Max time complexity = O(n)
public static int[] generate(int n, long k) {
// generate starting sequence of length n with no inversions
final int[] a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = i;
}
// nothing to do
if (k == 0) {
return a;
}
/**
* Example:
*
* n = 6
*
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 -> 5 0 1 2 3 4 == 5 inversions (1 swap)
* 5 0 1 2 3 4 -> 5 4 0 1 2 3 == 9 inversions (2 swaps)
* 5 4 0 1 2 3 -> 5 4 3 0 1 2 == 12 inversions (3 swaps)
* 5 4 3 0 1 2 -> 5 4 3 2 0 1 == 14 inversions (4 swaps)
* 5 4 3 2 0 1 -> 5 4 3 2 1 0 == 15 inversions (5 swaps)
*/
// compute the number of swaps (as shown above example)
int minSwap = 0;
int inversionCount = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
final int newInversions = (n - i);
if ((inversionCount + newInversions) <= k) {
minSwap++;
inversionCount += newInversions;
} else {
break;
}
}
// perform min swaps (bulk inversions)
for (int i = 0; i < minSwap; i++) {
a[i] = (n - 1) - i;
}
// fill in remaining numbers
for (int i = 0; i < (n - minSwap); i++) {
a[minSwap + i] = i;
}
// do remining individual inversions
for (int i = 0; (i < (n - minSwap)) && (inversionCount < k); i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; (j < (n - minSwap)) && (inversionCount < k); j++) {
// swap to create inversion
final int temp = a[minSwap + i];
a[minSwap + i] = a[minSwap + j];
a[minSwap + j] = temp;
inversionCount++;
}
}
return a;
}
// Takes an integer n and a long k as command-line arguments,
// and prints a permutation of length n with exactly k inversions.
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
final long k = Long.parseLong(args[1]);
final int[] a = generate(n, k);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Link To: Java Source Code