Coursera - Computer Science: Programming With A Purpose
Week 4: Functions - Greatest Common Divisors
Write a program Divisors.java to compute the greatest common divisor and related functions on integers:
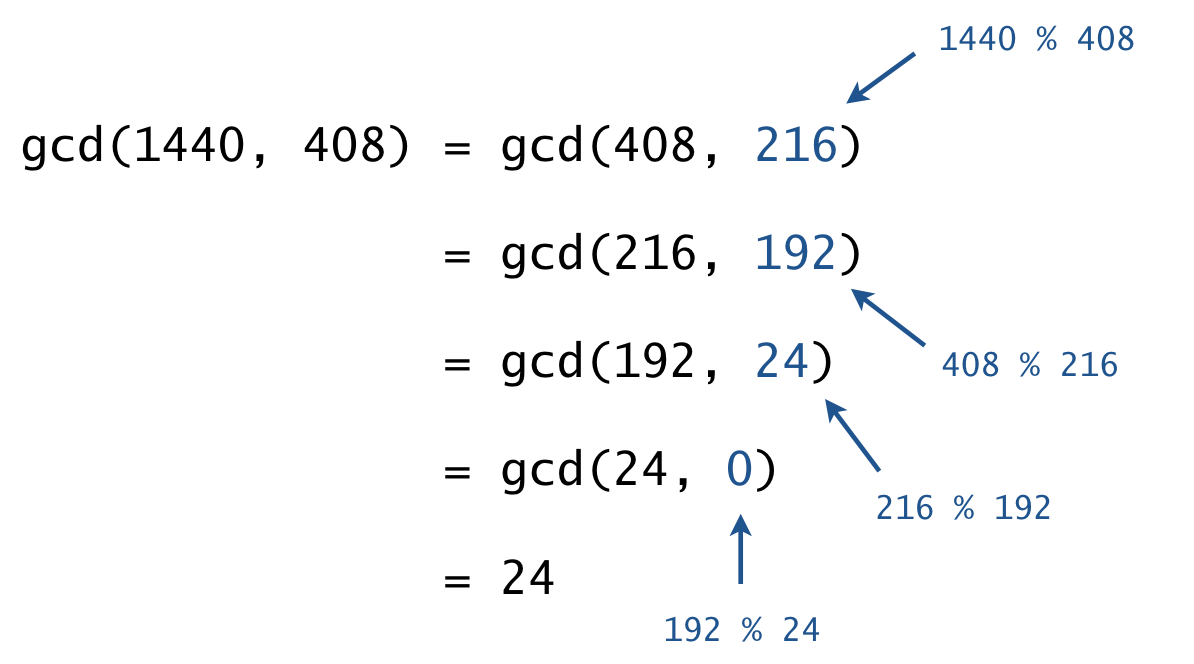
- The greatest common divisor (gcd) of two integers a and b is the largest positive integer that is a divisor of both a and b. For example, gcd(1440, 408) = 24 because 24 is a divisor of both 1440 and 408 (1440 = 24 * 60, 408 = 24 * 17) but no larger integer is a divisor of both. By convention, gcd(0,0) = 0.
- The least common multiple (lcm) of two integers a and b is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of both a and b. For example, lcm(56, 96) = 672 because 672 is a multiple of both 56 and 96 (672 = 56 * 7 = 96 * 12) but no smaller positive number is a multiple of both. By convention, if either a or b is 0, then lcm(a, b) = 0.
- Two integers are relatively prime if they share no positive common divisors (other than 1). For example, 221 and 384 are not relatively prime because 17 is a common divisor.
- Euler’s totient function ϕ(n) is the number of integers between 1 and n that are relatively prime with n. For example, ϕ(9) = 6 because the six numbers 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, and 8 are relatively prime with 9. Note that if n ≤ 0, then ϕ(n) = 0.
To do so, organize your program according to the following public API:
public class Divisors {
// Returns the greatest common divisor of a and b.
public static int gcd(int a, int b)
// Returns the least common multiple of a and b.
public static int lcm(int a, int b)
// Returns true if a and b are relatively prime; false otherwise.
public static boolean areRelativelyPrime(int a, int b)
// Returns the number of integers between 1 and n that are
// relatively prime with n.
public static int totient(int n)
// Takes two integer command-line arguments a and b and prints
// each function, evaluated in the format (and order) given below.
public static void main(String[] args)
}
Here are some sample executions:
~/Desktop/functions> java Divisors 1440 408
gcd(1440, 408) = 24
lcm(1440, 408) = 24480
areRelativelyPrime(1440, 408) = false
totient(1440) = 384
totient(408) = 128
~/Desktop/functions> java Divisors 987 610
gcd(987, 610) = 1
lcm(987, 610) = 602070
areRelativelyPrime(987, 610) = true
totient(987) = 552
totient(610) = 240
Use the following algorithms to implement the corresponding functions.
- Greatest common divisor. Implement an iterative version of Euclid’s algorithm.
To compute the greatest common divisor of a and b:
- Replace (a, b) with (abs(a), abs(b)).
- Repeatedly replace (a, b) with (b, a % b) until the second integer in the pair is zero.
- Return the first integer in the pair as the gcd.
-
Least common multiple. Use the following formula, which relates the gcd and lcm functions: lcm(a, b) = (abs(a) * abs(b)) / gcd(a, b) To avoid preventable arithmetic overflow, perform the division before the multiplication. Recall that lcm(0, 0) = 0.
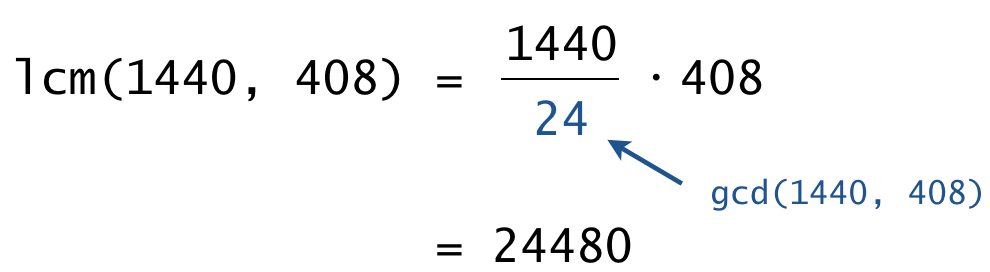
- Relatively prime. Two integers a and b are relatively prime if and only if gcd(a, b) = 1.
- Euler’s totient function. Use the definition and call areRelativelyPrime() for each positive integer between 1 and n.
The greatest common divisor and least common multiple functions arise in a variety of applications, including reducing fractions, modular arithmetic, and cryptography. Euler’s totient function plays an important role in number theory, including Euler’s theorem and cyclotomic polynomials.
Note: the above description is copied from Coursera and converted to markdown for convenience
Solution:
public class Divisors {
// Returns the greatest common divisor of a and b.
public static int gcd(int a, int b) {
a = Math.abs(a);
b = Math.abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
int mod = a % b;
a = b;
b = mod;
}
return a;
}
// Returns the least common multiple of a and b.
public static int lcm(int a, int b) {
if ((a == 0) && (b == 0)) {
return 0;
}
return Math.abs(a) * (Math.abs(b) / gcd(a, b));
}
// Returns true if a and b are relatively prime; false otherwise.
public static boolean areRelativelyPrime(int a, int b) {
return gcd(a, b) == 1;
}
// Returns the number of integers between 1 and n that are
// relatively prime with n.
public static int totient(int n) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (areRelativelyPrime(i, n)) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
StdOut.println("gcd(" + a + "," + b + ") = " + gcd(a, b));
StdOut.println("lcm(" + a + "," + b + ") = " + lcm(a, b));
StdOut.println("areRelativelyPrime(" + a + "," + b + ") = " + areRelativelyPrime(a, b));
StdOut.println("totient(" + a + ") = " + totient(a));
StdOut.println("totient(" + b + ") = " + totient(b));
}
}
Link To: Java Source Code